
ExtruVis - Optical residence time distribution measurement and automated evaluation
Measuring your residence time distributions has never been easier

What is ExtruVis?
ExtruVis is an instrument to measure Residence Time Distribution (RTD) in any possible application in which a visual tracer can be applied. After adding the tracer, ExtruVis records a video of the experiment. Once the measurement is completed, ExtruVis evaluates the RTD automatically.








Tracer + Input
Output
Optical path
Led ring light
Camera
Tripod

Vacuum Unit
What do you need to know?
The basics.
The residence time distribution (RTD) is the probability of how long stream elements remain inside a continuous process. Chemical engineers use RTDs to characterize mixing and flow behaviors. The results are compared with ideal behaviors and used for designing and troubleshooting.





The theory of RTD
From theory to practice
Risks in continuous processing
Identifying via RTD measurement
The theory of RTD

Engineers like to simplify real processes with ideal models. Ideal models have either perfect mixing or equivalent time spans inside the processing equipment.
VS
Ideal Flow
Real Flow

a
Continuous
stirred-tank reactor
(CSTR)
Inlet
Outlet


b
c
Plug-flow reactor (PFR)
Inlet
Outlet
Tube
Inlet
Outlet
Baffle
Recirculation
Complex geometry
Stagnant zone
Shortcutting
Real processes have imperfect mixing, dead zones, and shortcuts within the equipment, making them difficult to describe.

From theory to practice
An easy to perform experiment can be conducted to gain insights into the flow behavior of a real process. A color tracer is applied at the inlet at time zero (t=0). The response is recorded at the outlet. The shape of the response is the residence time distribution.
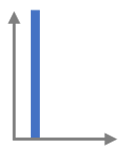
Ideal Impulse
Ideal Responses
VS
Real Response
Inlet
Color Tracer Input

*
RTD

*

*
RTD
RTD
CSTR
a
PFR
b
c
Inlet
t = 0
t = 0
t = 0
t = t1
Time
* grey bar shows the input impulse as reference
Why it is important for you?
Quality ensuring insights.
Mixing, Content Uniformity (CU), and degradation are important terms in continuous processing. All are linked to the RTD, and all processes have their own characteristics. RTD measurements are contributing to deep process understanding and well-defined design spaces.

Risks in continuous processing
CU problems cause high costs and can be very difficult to identify. Good mixing is required to obtain good CU and ensure that every tablet contains the required ingredients. Excessive mixing might cause temperature-induced degradation.
A
B
Bad mixing
Good mixing
Over mixing

Sample
CU
Sample
CU
Sample
Stressed
Good CU


Bad CU
CU

RTD measurements can be performed either on single-unit operations (UO) or on several combined UOs up to complete processing lines. Problems can be studied where they occur.
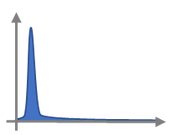
Identifying via RTD measurement
time
RTD
time
time
RTD
RTD


Bad mixing
Good mixing
Degradation
Problems can be caused by the fluctuation of a feeder, which was not dampened out by the mixing capabilities of the subsequent steps. A newly formed bypass stream prevented good mixing or degradation occurred due to extensive recirculation.
What is ExtruVis used for?
Not only for extrusion.
Continuous processes are applied in almost every industry to manufacture or process materials without interruption. It works on all scales, with small lab and large production equipment. Comparable RTDs ensure successful scale-up. Below are applications which were published by our customers.





Granulation
Extrusion
Continuous blending
Roller compaction and milling

Granulation
The screw design can dampen feeding fluctuations as long as they are clearly smaller than the width of the RTD. Feeding units can cause problems.

Meier, Thommes, Rasenack, Moll, Krumme, Kleinebudde
Out-of-spec granules can occur when one substance is not fed at the appropriate rate for several seconds.
Bochmann, Steffens,
Gryzcke, Wagner

Extrusion
Simulations are widely applied to design hot melt extrusion processes in-silico. Many assumptions have to be made, and most material characteristics are unknown in the early stages.

Validation experiments are performed to check if the assumptions were correct and the simulation data is reliable.
Is there more?
Continuously more.
ExtruVis can be used to study individual unit operations or complete process chains. It provides insights for troubleshooting or for characterization and process design purposes. By using ExtruVis, a clear analysis will be generated.
Continuous blending



Blenders are often fed by dosing units that discharge the material in a pulsating way, e.g., an auger screw.
The continuous blender must compensate for the pulsation to ensure homogeneous results. A wide RTD is beneficial to smooth out deviations.

Roller compaction and milling
Mangal, Kleinebudde
Fine tracer particles were able to pass through equipment without the mill equipment running.

Dry granulation consists of unit operations, roller compaction, and milling. Mangal investigated the milling step via RTDs. It was found that a conical mill had shorter residence times compared to an oscillating mill.
How does it work?
In four steps.
ExtruVis is a complete solution for carefree measurement of residence time distributions. Everything you need is included and packed into a robust and easy to transport trolley. Take it directly to the processing equipment and follow the four steps below to obtain the RTD insights.

Step 1: Setup
Step 3: Measurement

Locate the ExtruVis camera in the vicinity of the process. Turn on the ring light, object the field of view, and set the camera parameters.

Step 2: Adding the tracer
Start the measurement on the laptop. After 10 seconds, the operator has to add tracer to the process. The time point is signalized by an acoustic beep.
ExtruVis records the color information of the ROI (Region Of Interest). The live view cockpit is showing you the data in real-time and enables a precise and reliable determination when the tracer is washed out.






The Region Of Interest (ROI) is captured by the ExtruVis software to have a reference value.
Step 4: Analyze your data
ExtruVis will guide you through the analysis of the recorded measurement and give you access to results within seconds.
Automatic Detection and Evaluation


Difficult evaluation?
Not at all.
ExtruVis empowers the operator to describe the color information in a quantitative manner in real time. The start and end point of the RTD experiment are determined precisely. The evaluation is performed by a sophisticated algorithm, which ensures reproducible results after a few clicks.
What are the results?
Answers.
A picture is worth a thousand words. This is true for RTD measurements. The RTD curves tell you more than single values. RTDs are usually evaluated either via curve evaluation or model-based evaluation. Both methods create data that can be used as a tool for process design or troubleshooting.

Analytical curve evaluation
The analytical evaluation of the parameters is performed by statistical curve evaluation, which describes the shape and dimensions of the parameters based on analytical measurements.

For simplicity‘s sake, standardized measurement parameters are defined to make them quickly comparable with tmean. For in-depth analysis, a complete overlapping is recommend.

VS

A slight change, which is not detectable by the naked eye, is reliably detected by ExtruVis, revealing a flow error like a bypass stream.
What can you tell your friends?
A pun.
A sophisticated multistep regression approach fits the model parameter towards a model system to optimally represent the measured data set. In that matter next time you can tell your friends, “I work with models”.
Model-based evaluation
The combination of ideal models can be used to represent real processes. ExtruVis uses a series of plug flow reactors and continuously stirred tank reactors to represent the measured data.
Plug flow fraction
The fluid that does enter the reactor system flows in plug flow.
Number of continuous stirred-tank reactors (CSTRs)
The parameter n is the number of CSTRs in series used for the model to describe the experimental measured RTD.
Dead zone fraction parameter
The dead zone fraction parameter d describes the fraction in the process where no mixing and no conveying occurs.
But there are many more values like the Back Mixing Quality, Bodenstein number, and Peclet number.

Plug flow reactor
Continuous stirred-tank reactor Cascade


The parameters of the models as well as dimensionless numbers (PE, Bo) are clearly summarized in a table.
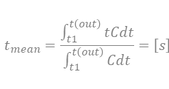
What do I get?
Everything you need.
We believe that simplicity is the key to efficiency. That’s why ExtruVis technology comes as an all-around carefree package packed in a handy trolley. It contains all the necessary equipment needed to measure the RTD.


Combined camera and light unit
The unit consists of a USB camera and a ring-light. The circular light provides a uniform, reflection- and shadow-free illumination of the region of interest (ROI). Precise color measurement guaranteed.

The camera lens is suitable for RTD measurements on all scales. Two configurations allow measurements from a lab (mm² range) to production scale (cm² range).
High-pigmented tracer

High-pigmented tracers in RGB (red, green, and blue) are included. The tracers are thermally stable single molecule food grade colors. Other tracers are possible if they give enough visual response at the outlet.

Color concentration correlation
Only very small amounts are needed for the experiments. A rule of thumb for the tracer amount is to take 1-3% of the mass flow which enters per second.
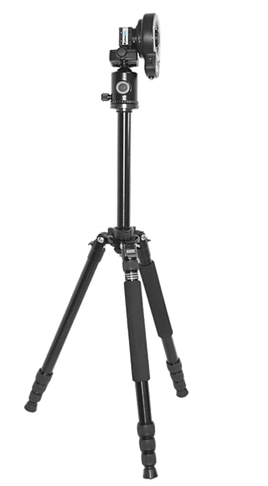
Versatile tripod enabling the best view
The tripod allows various mouting options. It can be adjusted in several versatile ways.




Is training required?
Only with the simulator.
We understand that the operation of an instrument must be learned before it can be used with confidence. We included an RTD simulator for gaining the confidence before you run an expensive experiment.

Laptop with ExtruVis & RTD simulator
The ExtruVis system contains a laptop with the ExtruVis software preinstalled. It is easy to use, gives you quick results from one experiment, and allows raw data export for advanced evaluation.


RTD simulation printed color bars.
The simulator is a programable rotating cylinder with a printed color gradient and mimics the outlet of a continuous process.
What makes pilots and experts successful?
A simulator.
ExtruVis carefree package contains a Residence Time Distribution simulation kit to help you run your future experiment with confidence. Train with simulator to achieve the best results!
What are the advantages?
Less effort.
The various advantages of ExtruVis can be summarized with the two words above. ExtruVis was developed with one crucial premise in mind: It should make the life of a process engineer easier. Our motivation is to provide you with the tools that enable you to concentrate entirely on your project.

Standardized solution for all scales
There was no standardized method for measuring RTD before ExtruVis was on the market. With the help of ExtruVis, you can rely on reproducible data based on quantitative measurements and compare the RTDs of processes on different scales.
Conventional:


Defined shadow-free light source
The unique ExtruVis LED ring-light circularly mounted on the camera decouples the light conditions of the process under investigation from the ambient light sources (e.g. ceiling lamp, sun, etc.).

Conventional:
Shadows and ambient light effects affecting measurements.
Is that all?
Not even close.
ExtruVis is made of hand-picked materials to ensure best usability and quality. Our engineers have thought about every aspect down to the smallest detail, such as including an RGB color tracer set in the convenient ExtruVis package so that you can start measuring immediately.

Real-time data evaluation
No long waiting time for the evaluation, no tedious reworking of the results. During the measurement, you can follow a live chart on your laptop showing all the relevant data. The evaluation is completed within seconds and stored as a .csv file.
Conventional:

Better than the naked eye
ExtruVis is superior to the human eye and a reliable way to obtain accurate RTD results. Time points like peak and washed-out time are important for constructing RTDs but lie in regions of subtle changes and cannot be determined precisely with the stopwatch approach.

Inaccurate stopwatch approach.
No quantitive color information.

Conventional:
About ExtruVis
ExtruVis was developed by Andreas Gryczke and became part of the MeltPrep family in 2019.
"Measuring residence time distribution was not easy in the past. As an engineer, I know that RTD contains important process development, understanding, and troubleshooting parameters. I focused on making these parameters easily accessible for other professionals in various fields."

(Andreas Gryczke, Founder ExtruVis)


